Viruses or Bacteria? What got you sick?
When you use antibiotics correctly, you do the best for your health, your family’s health, and the health of those around you.
Here are tips for how to use antibiotics correctly.
Ask if an Antibiotic is Necessary
Say YES to antibiotics when needed for certain infections caused by bacteria.
Say NO to antibiotics for viruses, such as colds and flu, or runny noses, even if the mucus is thick, yellow or green.
Antibiotics also won’t help for some common bacterial infections including
- most cases of bronchitis,
- many sinus infections, and
- some ear infections.
When they’re not needed, antibiotics won’t help you, and the side effects could still hurt you.
Never pressure your healthcare professional to prescribe an antibiotic.
30% of antibiotics are prescribed unnecessarily in doctors’ offices and emergency departments in the United States.
Know What’s Got You Sick
Antibiotics cure bacterial infections, but not viral infections such as:
- Colds or flu
- Most coughs and bronchitis
- Most sore throats
- Runny noses, even if the mucus is thick, yellow or green
Taking antibiotics for viral infections:
- Will not cure the infection
- Will not keep other people from getting sick
- Will not make you feel better
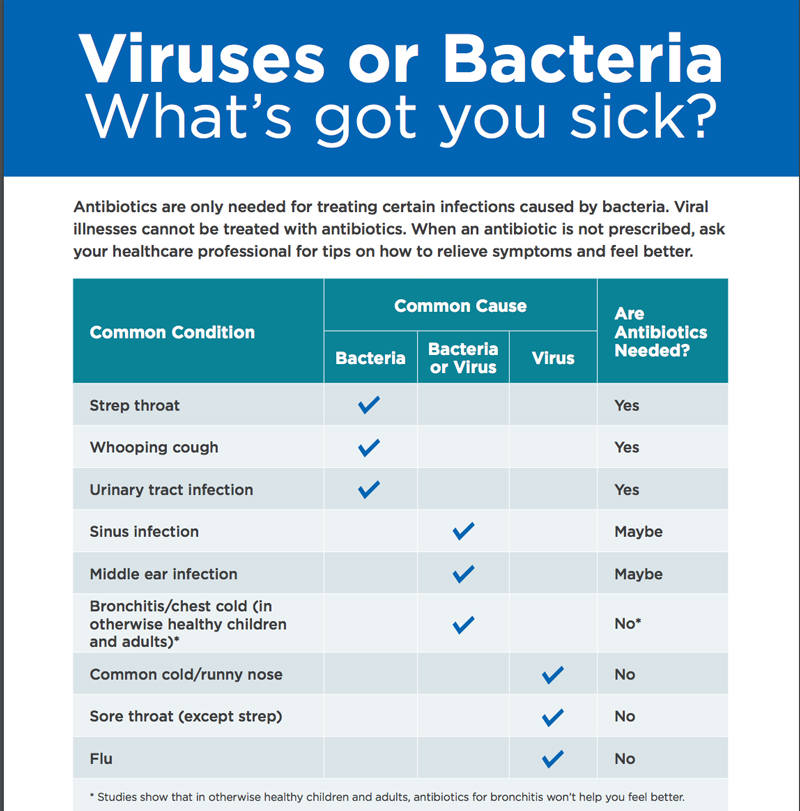
| Common Condition: What’s got you sick? | Common Cause Bacteria |
Common Cause Bacteria or Virus |
Common Cause Virus | Are antibiotics needed? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strep throat | ✔ | Yes | ||
| Whooping cough | ✔ | Yes | ||
| Urinary tract infection | ✔ | Yes | ||
| Sinus infection | ✔ | Maybe | ||
| Middle ear infection | ✔ | Maybe | ||
| Bronchitis/chest cold (in otherwise healthy children and adults)* | ✔ | No | ||
| Common cold/runny nose | ✔ | No | ||
| Sore throat (except strep) | ✔ | No | ||
| Flu | ✔ | No |
* Studies show that in otherwise healthy children and adults, antibiotics for bronchitis won’t help you feel better.
Know When Antibiotics Are Needed and When They’re Not
If you need antibiotics, take them exactly as prescribed.
Talk with your doctor if you have any questions about your antibiotics, or if you develop any side effects, especially diarrhea, since that could be Clostridium difficile infection (also called C. difficile or C. diff), which needs to be treated immediately. C. diff can lead to severe colon damage and death.
When antibiotics aren’t needed, they won’t help you, and the side effects could still hurt you. Side effects range from minor to very severe health problems. When you need antibiotics for an infection, then the benefits of the drug outweigh the risk of side effects.
Know How to Feel Better
Respiratory viruses usually go away in a week or two without treatment.
Sometimes the best treatment for your illness may be over-the-counter drugs to relieve your symptoms.
Ask your healthcare professional for tips on how to relieve symptoms and feel better while your body fights off the virus.
Know How to Stay Healthy
To stay healthy and keep others healthy, you can:
- clean hands,
- cover coughs,
- stay home when sick, and
- get recommended vaccines, for the flu, for example.
Safely Get Rid of Your Medications
Safely throw away leftover medication.
- Never save antibiotics for the next time you become sick.
- Prevent children from finding and swallowing your medication
- Do not take antibiotics prescribed for someone else. This may
- delay correct treatment for you,
- make you even sicker, or
- cause bad side effects.
Know What to Ask Your Child’s Doctor
If your child is sick, here are three important questions to ask your healthcare professional:
In children, reactions from antibiotics are the most common cause of medication-related emergency department visits.
- What is the best treatment for my child’s illness?
Your child can feel better without an antibiotic. Respiratory viruses usually go away in a week or two without treatment. Ask your healthcare professional about the best way to feel better while your child’s body fights off the virus. - What do I need to know about the antibiotics you’re prescribing for my child today?
If your doctor says your child needs an antibiotic, ask if it’s the one most targeted to treat the infection, while causing the least side effects. Some types of antibiotics, such as fluoroquinolones, have a stronger link to severe side effects such as life-threatening C. diff infections. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) warns healthcare professionals to only prescribe fluoroquinolones when another treatment option is unavailable. These powerful antibiotics are often prescribed even when they are not the recommended treatment. - What can I do to help my child feel better?
Pain relievers, fever reducers, saline nasal spray or drops, warm compresses, liquids, and rest may be the best ways to help your child feel better. Your healthcare professional can tell you how to help relieve your child’s symptoms.
Source: CDC 5/2018 https://www.cdc.gov/
Yours in Service,
Rachel Huerta, ARNP
Owner of Direct Primary Care of Boca Raton
2017 Healthcare Woman of Distinction Award Winner
Immediate Past-President of The Rotary Club of Boca Raton
